
Researchers of the innovative team for genetic breeding of bast fiber crops from the Institute of Bast Fiber Crops, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, combined the artificial floating island technology with ramie heavy metal remediation technology, and systematically studied the effects of different conditions on the remediation of cadmium pollution in paddy fields. This study provided innovative technical routes and practical experience for the research in the field of phytoremediation of heavy metal pollution.
Ramie ( Boehmeria nivea L.) is an ideal crop for cadmium (Cd) pollution remediation due to its advantages of both remediating and utilizing, however, it is mainly carried out in dry land, whose restoration effect is relatively slow. Previously, the research team found that the ramie plants cultivated by hydroponics has several tens of times higher Cd absorption capacity than that planted in soil. However, the issue of how to use hydroponic ramie to remediate Cd contaminated paddy fields needs to be addressed.
The research team innovatively developed the ramie floating island technology and studied its remediation model on simulated Cd contaminated paddy fields. Different ramie varieties were used to compare the remediation effects, and the results showed that there were differences in adaptability among different varieties on floating islands and the remediation ability of the tested ramie varieties was Z2 > Z1 > Z3. Different harvested times were set to analyze the effects of harvested model on remediation, and it was suggested that multiple harvests can be carried out according to the plant growth status of ramie floating island after 30 days of remediation to achieve better remediation effects. Low water level height (5 cm) of paddy field was beneficial for the accumulation of Cd in the roots, but considering the adaptability of various ramie varieties and the effect of long-term restoration, it was recommended that the water level height of 20 cm for the cultivation of ramie floating island was more suitable. Moreover, we found that low concentration of citric acid (≤ 2 g/L) or polyaspartic acid (≤ 3 g/L) can improve the remediation effects for ramie floating island. This study opens up a novel approach for ramie to remediate heavy metal pollution and provides a technical reference for water body Cd remediation by plants.
This research was funded by the Natural Science Foundation of Hunan province, China Agriculture Research System of MOF and MARA, and the Science and Technology Innovation Project of Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences.
The study entitled Study on remediation of cadmium contaminated paddy field by ramie (Boehmeria nivea L.) floating island and its supporting technology has been published online in Environmental Research journal and can be accessed through the following link https://authors.elsevier.com/sd/article/S0013-9351(23)02602-6 .
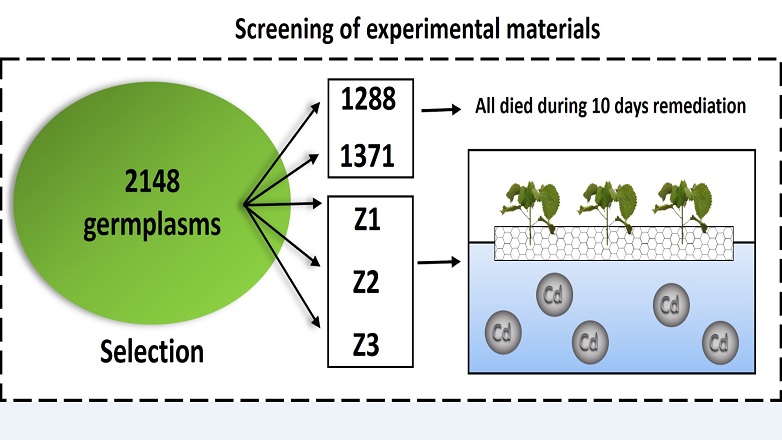
Fig. Screening of ramie varieties

