
作者:Ningyang Li, Xueyu Zhang, Xiudong Sun, Siyuan Zhu, Yi Cheng, Meng Liu, Song Gao, Jiangjiang Zhang, Yanzhou Wang, XiaiYang, Jianrong Chen, Fu Li, Qiaoyun He, Zheng Zeng,Xiaoge Yuan, Zhiman Zhou, Longchuan Ma, Taotao Wang, Xiang Li, Hanqiang Liu, Yupeng Pan, Mengyan Zhou, Chunsheng Gao, GangZhou, Zhenlin Han, ShiqiLiu, Jianguang Su, Zhihui Cheng, Shilin Tian and Touming Liu.
影响因子:10.465
刊物名称:Genome Biology
出版年份:September 2022
doi: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13059-022-02756-1
Abstract
Background: Garlic is an entirely sterile crop with important value as a vegetable, condiment,and medicine.However, the evolutionary history of garlic remains largely unknown.
Results: Here we report a comprehensive map of garlic genomic variation,consisting of amazingly 129.4 million variations. Evolutionary analysis indicates that the garlic population diverged at least 100,000 years ago,and the two groups cultivated in China were domesticated from two independent routes. Consequently, 15.0 and 17.5% of genes underwent an expression change in two cultivated groups, causing a reshaping of their transcriptomic architecture. Furthermore, we find independent domestication leads to few overlaps of deleterious substitutions in these two groups due to separate accumulation and selection-based removal.By analysis of selective sweeps, genomewide trait associations and associated transcriptomic analysis,we uncover differential selections for the bulb traits in these two garlic groups during their domestication. Conclusions: This study provides valuable resources for garlic genomics-based breeding, and comprehensive insights into the evolutionary history of this clonal-propagated crop.
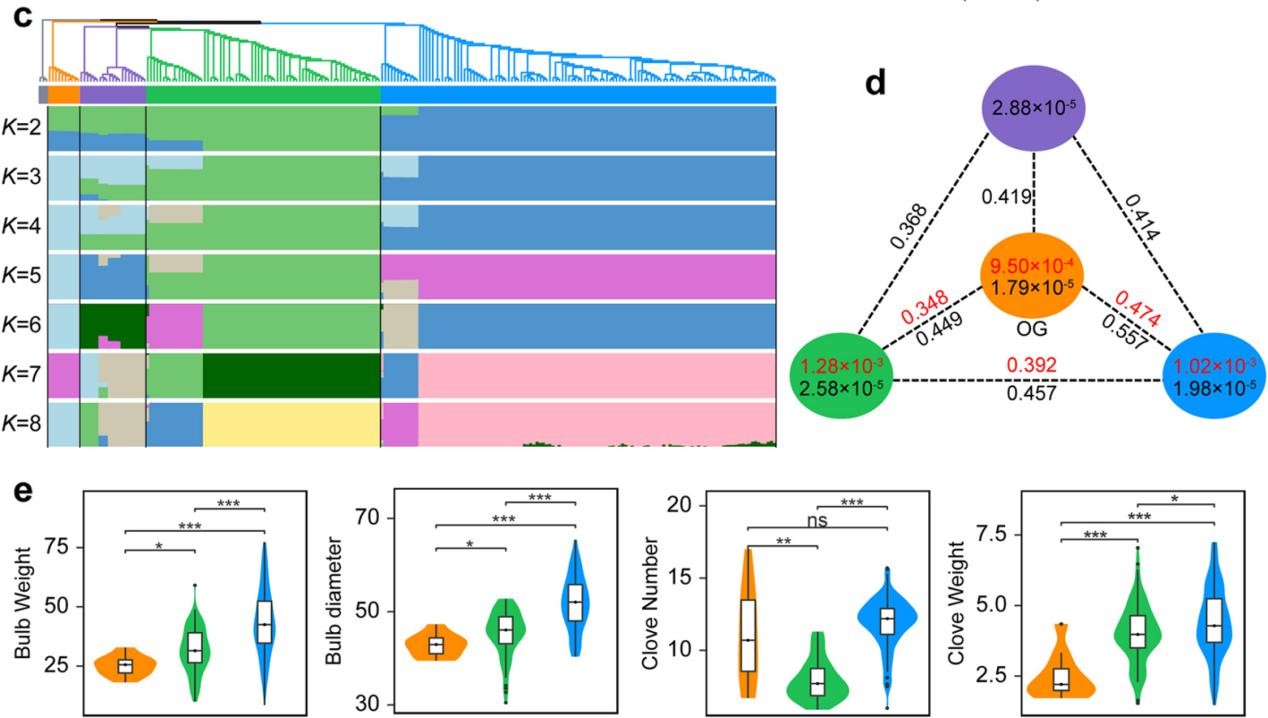
Fig. Population structure and genetic diversity of garlic accessions

